Monitoring Kubernetes cert-manager Certificates with BotKube

The monitoring and alerting stack is a crucial part of the SRE practices. That’s where BotKube helps you monitor your Kubernetes cluster and send notifications to your messaging platform or any other configured sink. In this blog post, we will be configuring BotKube to watch the Kubernetes cert-manager certificates CustomResources.
What is BotKube?
BotKube is a messaging tool for monitoring and debugging Kubernetes clusters. BotKube can be integrated with multiple messaging platforms like - Slack, Mattermost, or Microsoft Teams to help you monitor your Kubernetes cluster(s), debug critical deployments, and gives recommendations for standard practices by running checks on the Kubernetes resources.
What is cert-manager?
cert-manager helps you create and manage X.509 certificates in Kubernetes.
cert-manager builds on top of Kubernetes, introducing certificate authorities and certificates as first-class resource types in the Kubernetes API. This makes it possible to provide ‘certificates as a service’ to developers working within your Kubernetes cluster.
To achieve the above goal, cert-manager uses Kubernetes CustomResources.
How BotKube will help us monitor Kubernetes cert-manager certificates?
BotKube can monitor and notify us about the creation, deletion, and modification of Kubernetes resources. The v0.11+ of BotKube added support for the CustomResources as well. We will be using this feature to monitor the creation of new certificates and the rotation.
cert-manager also creates Kubernetes Kind Events related to the CustomResources. At the time of writing this post, BotKube can notify us about the Events of the type of Warning. Some examples include failure in renewing the certificates, issues in getting the CA TLS certificate for signing, and many more. Take a look at this GitHub repository search results to get a better idea about it.
Prerequisites
This post assumes that you already have a Kubernetes cluster with cert-manager and BotKube running on it. If you don’t have these things running, follow this section to get a minimal setup running on top of minikube. We will be configuring BotKube with Slack for this tutorial. You can use any other sink which supports the feature “K8s Event Push”.
Creating a Kubernetes cluster with minikube
- Install minikube on your machine by following the instructions given here.
-
To start the minikube cluster, run the following command.
$ minikube start * minikube v1.19.0 on Fedora 34 - KUBECONFIG=/home/bhavin/.kube/config * Using the kvm2 driver based on existing profile # … * Done! kubectl is now configured to use "minikube" cluster and "default" namespace by default
Install and setup BotKube
- Install Helm on your machine by following the instructions given here.
-
To add the infracloudio Helm chart repository, run the following command.
$ helm repo add infracloudio https://infracloudio.github.io/charts "infracloudio" has been added to your repositories $ helm repo update ...Successfully got an update from the "infracloudio" chart repository Update Complete. ⎈Happy Helming!⎈ - Install the BotKube Slack app in your workspace by following the instructions given in this section of the documentation. With this step, you will have a Slack token with you.
-
To create the Helm values file for BotKube, run the following command.
cat <<EOF > botkube-values.yaml communications: slack: enabled: true channel: "test" token: "<TOKEN_FROM_3>" config: settings: clustername: "bhavin-minikube" kubectl: enabled: true EOF -
To create a namespace and install BotKube, run the following command.
$ helm install botkube infracloudio/botkube \ --namespace monitoring --create-namespace \ -f botkube-values.yaml -
Verify that the pods are running.
$ kubectl get pods --namespace monitoring NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE botkube-684874499f-22mlz 1/1 Running 0 1m
If any of the above instructions don’t work, please take a look at the official documentation page for an updated version of these instructions.
Install cert-manager
-
To add jetstack Helm repository, run the following command.
$ helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io $ helm repo update -
To install cert-manager in cert-manager namespace, execute the following command.
$ helm install cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager \ --namespace cert-manager --create-namespace \ --set installCRDs=true -
Verify that the pods are running.
$ kubectl get pods --namespace cert-manager NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE cert-manager-7998c69865-dbfn4 1/1 Running 0 8m17s cert-manager-cainjector-7b744d56fb-drqgh 1/1 Running 0 8m16s cert-manager-webhook-7d6d4c78bc-d8t22 1/1 Running 0 8m17s
If any of the above instructions don’t work, please take a look at the official documentation page for an updated version of these instructions.
Let’s monitor the Certificates
Now that we have the basic understanding of cert-manager and BotKube, let’s configure BotKube to monitor the Certificates CustomResource of cert-manager.
Configuring BotKube
Add the following snippet under config in the botkube-values.yaml file.
# botkube-values.yaml
# config:
resources:
- name: cert-manager.io/v1/certificates
namespaces:
include:
- all
events:
- all
updateSetting:
includeDiff: true
fields:
- status.renewalTime
This configures BotKube to start monitoring the GVR (Group Version Resource) cert-manager.io/v1/certificates resource. Monitors all the operations like create, update, delete, error from all the namespaces.
We are also monitoring the status.renewalTime field of the Certificate object. This will create a notification when a certificate is renewed.
To update BotKube deployment, run the following Helm command.
helm upgrade botkube infracloudio/botkube -n monitoring -f botkube-values.yaml
You can read more about this configuration in the resource_config.yaml syntax documentation section.
Create a self-signed issuer and certificate
To test our changes, we will create a self-signed issuer and a certificate.
cat <<EOF > test-resources.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: cert-manager-test
---
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: test-selfsigned
namespace: cert-manager-test
spec:
selfSigned: {}
---
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: example-com
namespace: cert-manager-test
spec:
dnsNames:
- example.com
secretName: example-com-tls
issuerRef:
name: test-selfsigned
duration: 1h
renewBefore: 50m
EOF
Apply the manifest:
kubectl apply -f test-resources.yaml
# output
namespace/cert-manager-test created
issuer.cert-manager.io/test-selfsigned created
certificate.cert-manager.io/example-com created
The above command creates a namespace cert-manager-test along with a self-signed issuer. At the end, we are creating a Certificate that has a validity of 1 hour, and it gets renewed 50 minutes before its expiry. In other words, it will get renewed every 10 minutes.
If any of the above instructions don’t work, please take a look at the official documentation page for an updated version of these instructions.
This is how it will look on the Slack channel.
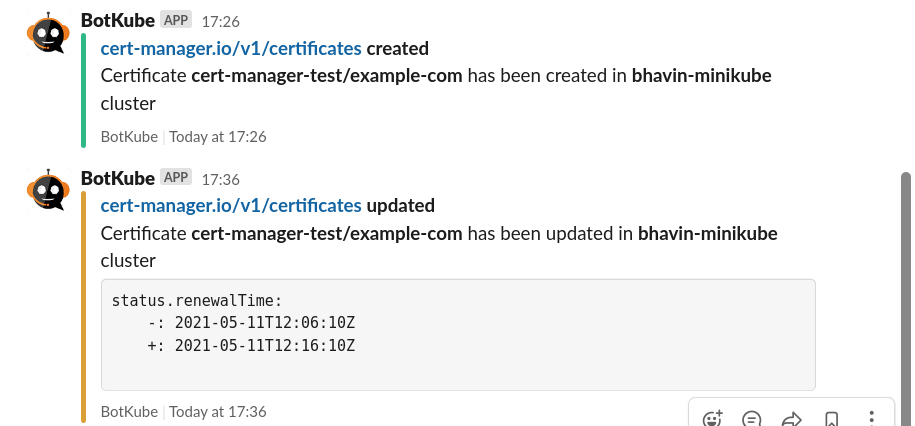
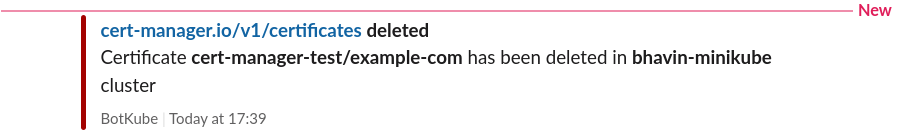
Let’s delete the Certificate resource and see what happens.
$ kubectl delete certificate example-com -n cert-manager-test
certificate.cert-manager.io "example-com" deleted
Conclusion
In this blog post, we took a look at the tools BotKube, cert-manager. We did the basic setup, configured BotKube to watch the Certificate resource of cert-manager. Similarly, we can configure BotKube to watch any of the CustomResources using this approach.
We hope you found this post informative and engaging. If you have questions, feel free to reach out to me on Twitter and start a conversation. New to BotKube? Join the BotKube community Slack. For regular cloud native updates from InfraCloud, follow us on LinkedIn.
Looking for help with observability stack implementation and consulting? do check out how we’re helping startups & enterprises as an observability consulting services provider.
Stay updated with latest in AI and Cloud Native tech
We hate 😖 spam as much as you do! You're in a safe company.
Only delivering solid AI & cloud native content.