Developing an AI Agent for Smart Contextual Q&A

Accelerated by the pandemic, online tech communities have grown rapidly. With new members joining every day, it’s tough to keep track of past conversations. Often, newcomers ask questions that have already been answered, causing repetition and redundancy. To tackle this, we built an intelligent assistant that tracks past conversations, searches Stack Overflow for technical help, and browses the web for relevant information.
InSightful is a ReAct (Reasoning and Action) Agent with access to multiple tools, such as a web searcher and a context retriever, to achieve the given task. In our case, it is a question and answer application. We will delve deeper into the workings of the application as we progress. At the end of the day, you will be able to understand how agents work and how you can develop your own. These agents are highly customizable, giving you a lot of flexibility in picking a use-case.
InSightul demo: Let’s see what InSightful can do
InSightful is meant to be an AI Agent that can smartly retrieve conversations from a workspace, search results on Stack Overflow with a given context and as well as browse the web whenever the information asked for is not available in the other two places. This makes sure that InSightful has a safety net to fallback on in case the intermediary response (thought and observation) does not match the user’s question. Let us see how we can develop such an application.
Prerequisites
- A GPU-enabled Kubernetes cluster OR a single GPU-enabled machine with Docker installed
- A HuggingFace account with a valid API key
- Three Services:
- TGI - Text Generation Inference
- TEI - Text Embeddings Inference
- Vector store - Chroma DB
Note: This tutorial assumes the developer has experience with Docker and understands how to use it appropriately. If the developer is using Kubernetes, this tutorial assumes they have a multi-node GPU cluster.
For the demo, we will be using a readily available HuggingFace dataset consisting of conversations from a workplace, simulating the real environment. The dataset mimics actual interactions amongst colleagues in tech communities like Slack workspaces, Reddit threads, or Discord servers. Downloading the dataset does not require any additional steps as it is included in the Python code.
Set up
In our set up, we are using a Kubernetes cluster that is already provisioned and completely set up to run AI workloads on.
If this is not your case, run the ai-stack separately on a GPU-enabled machine. If your machine is not equipped with a GPU, the inference will be extremely slow and is not recommended.
$ kubectl get svc -n ai-stack
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
tei LoadBalancer 10.233.22.94 192.168.0.203 80:32215/TCP 21h
tgi LoadBalancer 10.233.50.250 192.168.0.202 80:31963/TCP 21h
vectordb LoadBalancer 10.233.27.106 192.168.0.201 8000:30992/TCP 21h
(Kubernetes Services deployed using our AI stack chart)
Once each service is deployed and running, we can access their respective IPs and ports to send and receive data. Go ahead and clone the repo and follow the steps in the InSightful README file.
After successfully following the steps in the README, if all goes well, you should be greeted with this page on your browser:
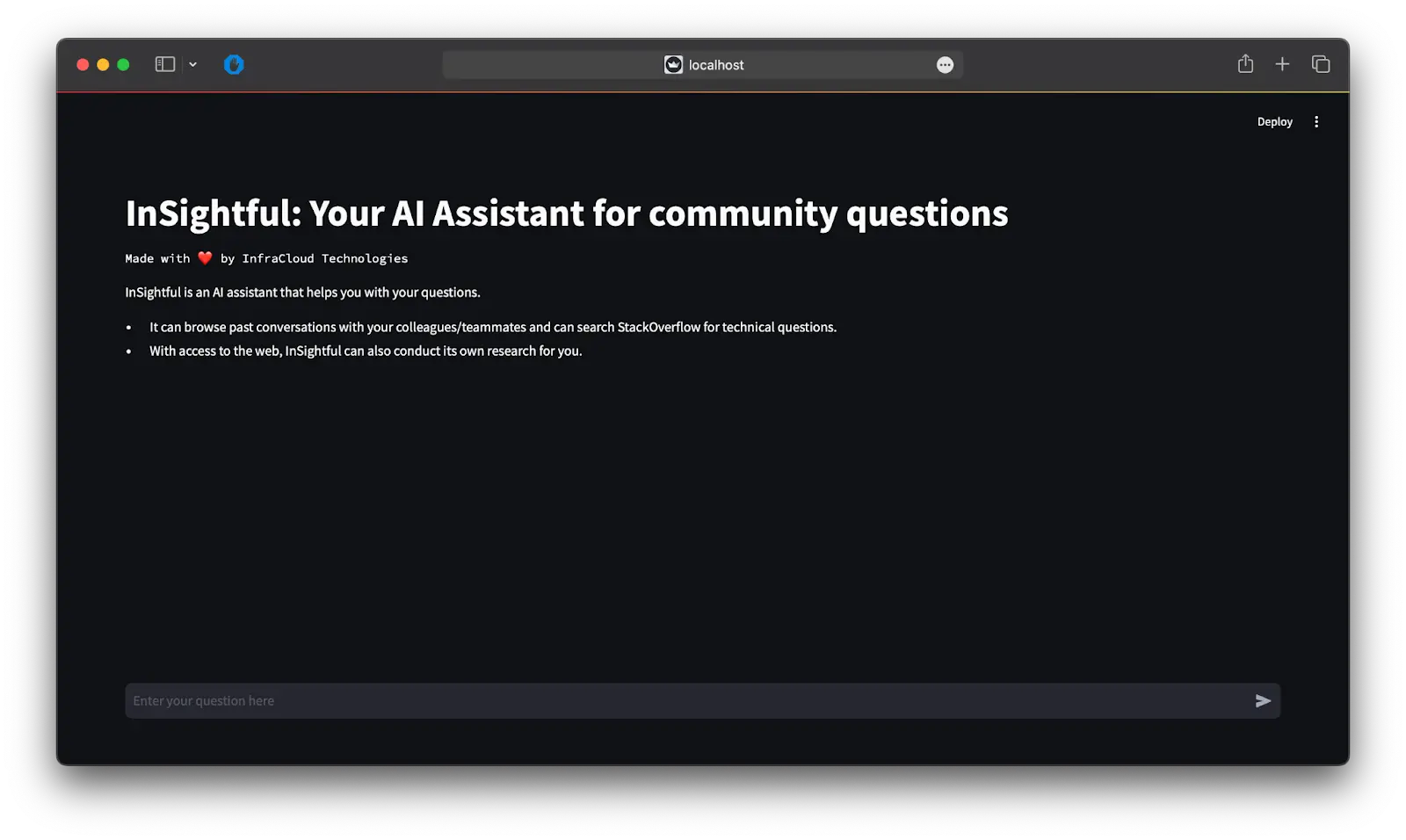
InSightful in action
Now, let’s see InSightful in action by asking it a question.You can ask different types of questions, according to the information you need.
-
Conversation analysis: InSightful can analyze and provide insights on the topics being discussed in tech communities. For example, if people are frequently discussing a specific programming language, it can highlight that.

(InSightful capturing details in Slack conversations) -
Community health analysis: InSightful can evaluate engagement, sentiment, and overall health of a tech community. It can show if people are generally positive or negative about certain topics.

(InSightful analyzing sentiments and overall community healths) -
Search Stack Overflow: InSightful can search Stack Overflow for relevant questions and answers, saving users time by providing instant solutions to common problems.

(InSightful responding to a technical question) -
Browse the web: InSightful can conduct web searches to gather relevant information on community topics, providing up-to-date knowledge.

(InSightful providing a response from web search results)
Now that we know what InSightful can do, let’s understand what it is, and how it works. As mentioned earlier, InSightful is powered by an AI Agent, so let’s begin with Agents.
Agents: A brief introduction
When ChatGPT was released, it quickly became popular, surpassing 1 millions users in just 5 days. Natural Language Processing (NLP) has been around for a while, but ChatGPT took it to the next level by turning a Language Model into a Large Language Model (LLM).
However, LLMs, while powerful language models, are like parrots—they repeat what they hear without real understanding. To make them more applicable to specific tasks and problems, we have to fine-tune, provide detailed prompts, and set guard rails to align their responses closely to the demands of the user. Developing agents exploit some of these approaches that enable them to reason and act accordingly. With a set of tools, an agent can perform actions on an environment, something a regular base LLM cannot achieve. Agents integrate these additional tools and frameworks, allowing them to perform specific tasks, make decisions, and interact dynamically with their environment.
For the sake of simplicity and to limit the scope of the InSightful demo, we will only be talking about the techniques we have employed to adapt the LLM to our own use case. We integrated LLM with web search and context retrieval tools, as well as provided a well-defined prompt. The combination of the prompt and the accessibility of the tools is what brings our agent to life. Something to note is that we don’t necessarily have to create an agent to utilize tools, instead, we can directly provide a compatible LLM with tools. We mention “compatible LLM” because not all LLMs are tool-calling enabled. However, with the help of LangChain, any LLM can be used to develop an agent to achieve the same results of tool-calling enabled LLMs. Ultimately, the LLM is used solely for reasoning and accessing a set of provided tools in a LangChain agent.
We prompted the agent cautiously and refined the prompt in several iterations, making it almost foolproof. The prompt makes the agent much more reliable in solving tasks, consistently abiding to a structure while forming its final response.
For InSightful, we took the Reasoning and Action (ReAct) Agent approach, which is a type of agent that can reason through a task, form an action plan to guide its actions and finally responds after thorough self-reflection. The incorporation of tools into the agent enables it to form effective responses.
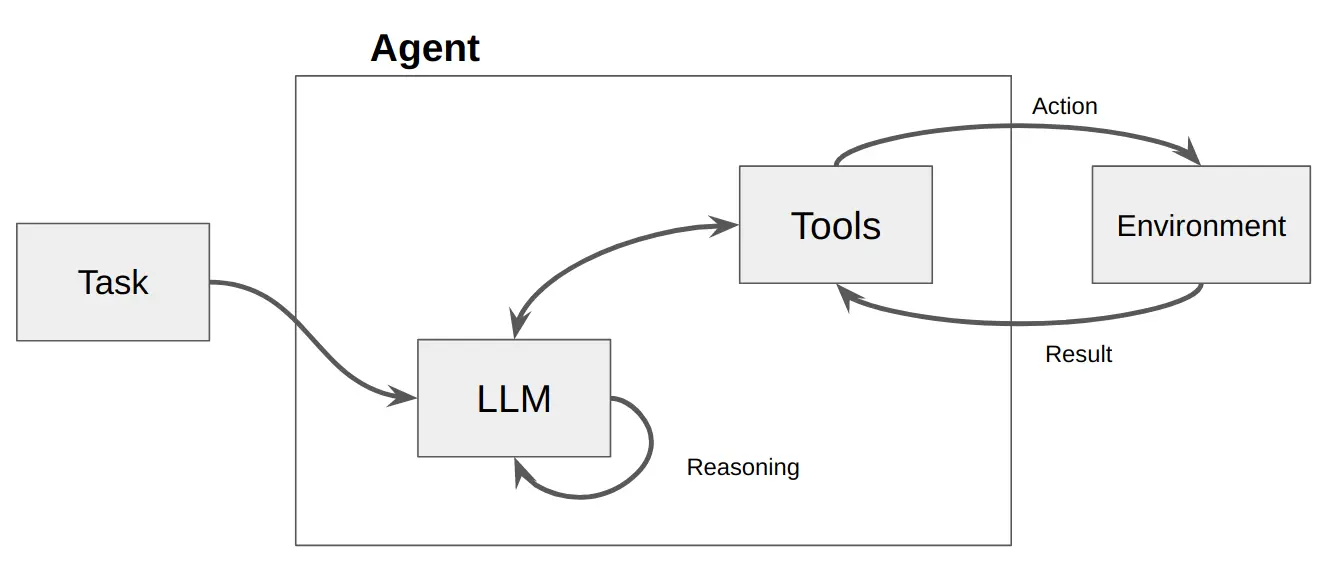
(Behind The Scenes of a ReAct agent)
From the diagram, we can understand that the task-in-hand is the question provided by the user and the environment is provided by the tool’s description. The tool’s description provides concise context to the agent to decide if a given tool is useful for the task or not. The cycle of “Thought-Action-Observation” is repeated a defined number of times until a satisfiable observation is made.
There are other alternatives to ReAct that are linear rather than ReAct’s cyclic approach such as Chain-of-Thought (CoT) and Tree-of-Thought (ToT), however, these alternatives do not support actions and will not enable learning from the consequences of the actions on an environment. They are purely reasoning-backed approaches.
Creating tools as functions
Fundamentally, tools are exactly what they sound like they are. They supplement the agent to generate accurate and contextual responses according to the user’s question. LangChain has an exhaustive list of such tools that can be integrated with agents.
InSightful applies several tools to enhance the agent:
-
Conversation Retriever tool: We converted the traditional Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) approach into a tool, making it more efficient for the agent. We essentially created our own tool, since the tool we want is not directly available in the LangChain package. This tool uses a vectorstore as its retriever, enabling similarity searches and predictions.This integration streamlines the process, allowing the agent to retrieve information without executing separate functions.
-
Stack Overflow search tool: We developed this tool using the Stack Exchange API, enabling the agent to search and query the extensive database of questions and answers on Stack Overflow.
-
Search engine tool: Tavily Search is a search engine tailored specifically for LLMs. We use the Tavily API integration with LangChain, which provides Tavily Search as a tool to use with LangChain agents.
Providing tools to our Agent
After creating these tools as callable functions, we compile them into a simple Python list like so:
tools = [retriever_tool, stack_overflow_search_tool, web_search_tool]
LangChain iterates over this list, using the name and description provided in each tool’s docstring to understand their purposes. Setting a name and description for each custom tool is mandatory as it provides LangChain with the context of what each function achieves.
Once we have our list of tools, we set it as a parameter when creating our agent. This setup indicates to the agent that it has access to these tools. When the agent determines which tool to use, it runs the corresponding function to trigger the tool. Ideally, the tool returns the desired results, and the agent uses that as additional context to augment its responses.
By integrating these tools, InSightful can:
- Retrieve and analyze conversations: Identify recurring questions and provide answers from past discussions, saving time and reducing redundancy.
- Engage in technical Q&A: Answer technical questions using Stack Overflow, giving quick and accurate responses.
- Conduct independent research: Browse the web for additional information on community topics, ensuring up-to-date and comprehensive answers.
Connecting the dots
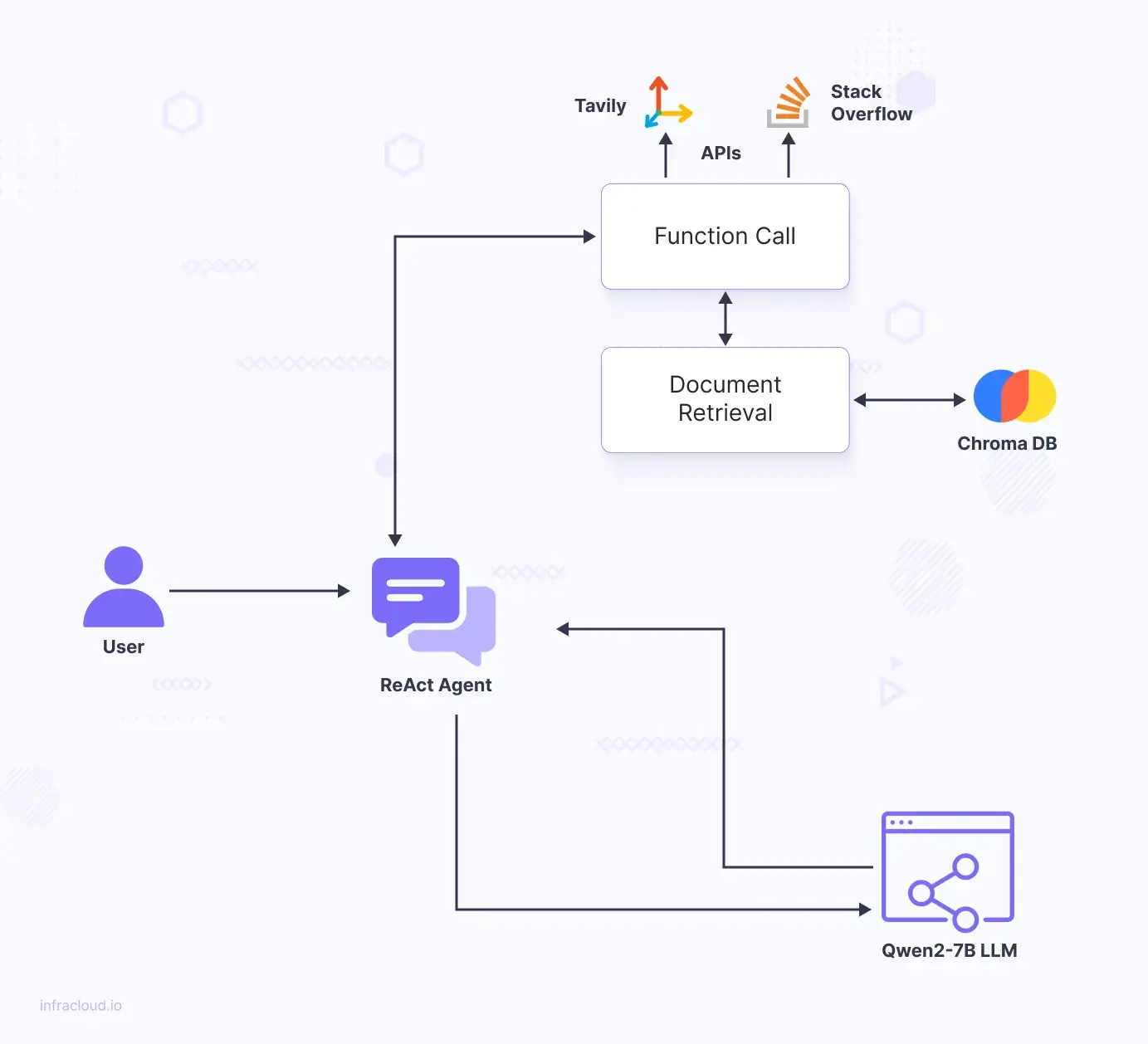
Let’s break down each of the components and how they fit into the big picture:
-
Document Retrieval: Retrieve conversation histories, technical questions, and other relevant data from a Data Source such as the vector store in our case.
-
Vector Storage: Vector Stores are where the embeddings are stored. The embeddings are generated by TEI.
-
LLM: TGI is where the LLM is running to generate responses based on the retrieved data, providing meaningful answers to user queries.
-
Tool/External API Integration: Integrate additional tools for searching Stack Overflow and browsing the web, expanding the assistant’s capabilities. The tools are powered by APIs offered by each of the services (Tavily and Stack Overflow).
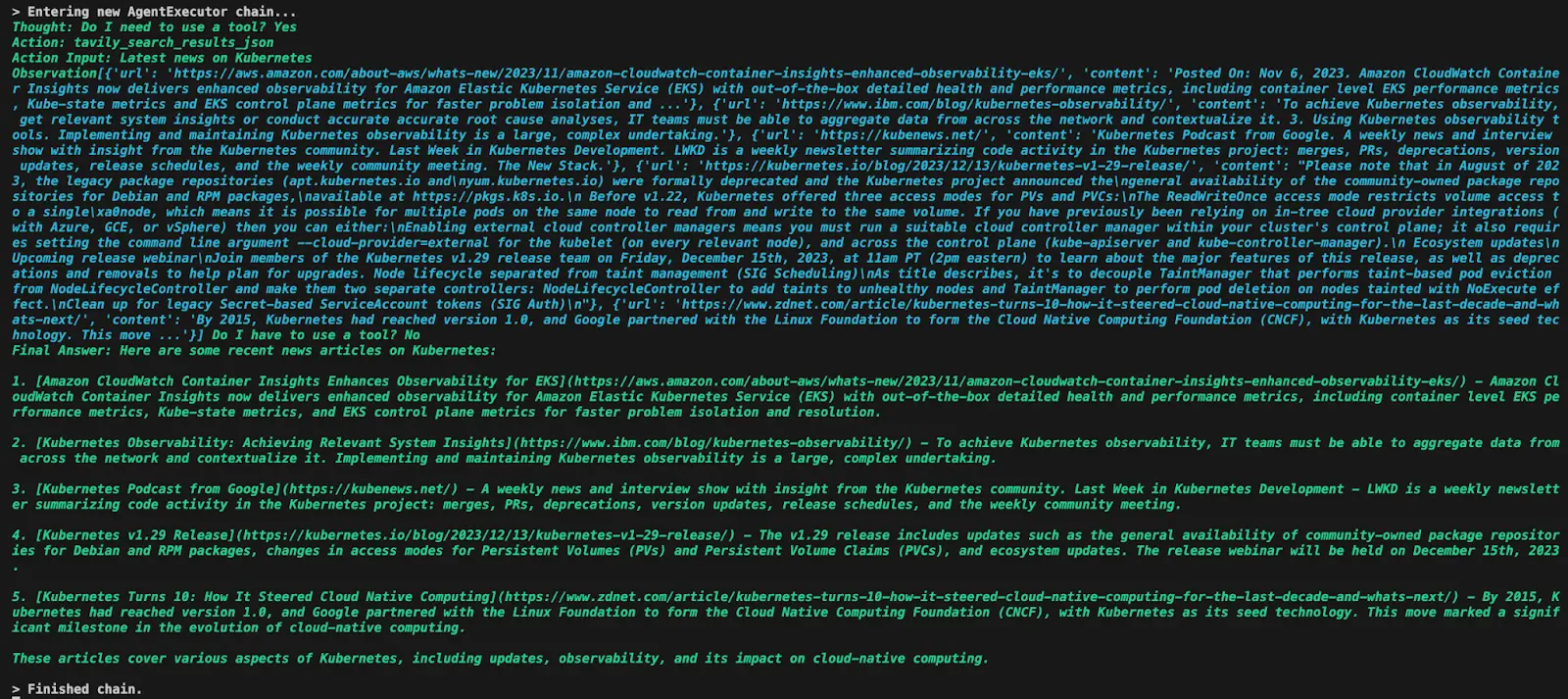
Here’s an example of the process when a user query is entered.The query “Latest news on Kubernetes” yields this result, only visible to the developer:
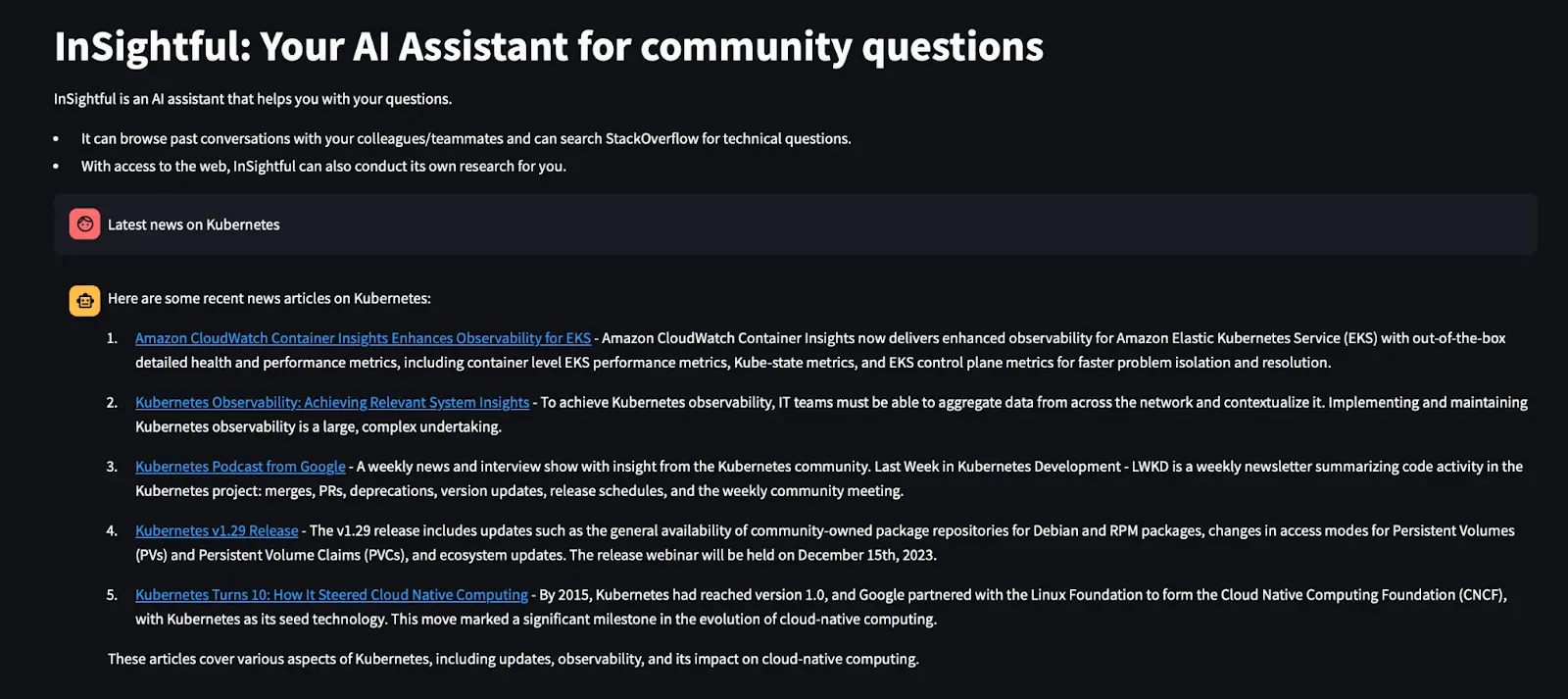
The user sees this on the front-end:
Benefits of the on-premise approach (local Kubernetes cluster)
InSightful works well in various online tech communities, such as Slack workspaces, Reddit threads, and Discord servers. The on-premise approach offers several advantages:
-
Data security: On-premise solutions provide enhanced security by keeping data within the organization’s own infrastructure, making it harder for remote hackers to access sensitive information. This level of control is especially crucial for industries with strict compliance requirements.
-
Customization: Organizations can tailor their hardware and software configurations to meet specific needs and compliance requirements. This allows for more specialized and efficient setups that cloud solutions might not offer.
-
Performance and low latency: Since the infrastructure is local, data processing and access times are faster. This is particularly beneficial for real-time applications or those handling large data volumes.
-
Control and ownership: Complete control over the hardware, software, and data ensures that organizations can implement their own security measures and protocols without relying on external providers.
Conclusion
InSightful uses state-of-the-art Generative AI to provide an intelligent assistant for tech communities and enterprises. By keeping track of past and present conversations, accessing Stack Overflow for technical questions, and browsing the web for additional research, InSightful reduces redundancy and improves the efficiency of information retrieval. This on-premise approach shows how integrating LLMs with specialized tools can create a practical and powerful AI assistant for enterprises. You can follow this article to build an AI Agent to power a conversation search and retrieval engine for your communication channels like Discord and Slack; however, having an efficient and scalable cloud infrastructure is crucial for building an AI application. AI & GPU Cloud experts can help you achieve this.
Hopefully, this has been as informative as we sought out to make it. Stay connected with us by subscribing to our weekly newsletter. Please share your valuable feedback with us, and we would love to hear from you on LinkedIn!
References
- LLM App dev framework - LangChain docs
- Tools used by InSightful - Tavily, Stack Exchange API, Chroma
- HuggingFace components - Text Generation Inference, Text Embeddings Inference
Stay updated with latest in AI and Cloud Native tech
We hate 😖 spam as much as you do! You're in a safe company.
Only delivering solid AI & cloud native content.