AI-Enabled Developer: A Complete Guide to Maximizing Development Productivity

The way we build software has changed significantly over the years. From traditional applications to the flexibility of cloud-native applications and now advancing into the Artificial Intelligence-native era, AI is redefining modern software practices by improving development pipelines and productivity.
Today’s teams are distributed worldwide and work with complex microservices, dependencies, and multiple cloud providers. Developers aren’t just writing code; they’re orchestrating systems. This is where AI integration becomes transformative, beyond just code completion. AI tools are essential partners in the development cycle and help teams manage complex tasks, automate routine tasks, and catch potential issues that reach production.
For developers, AI isn’t going to replace their expertise. It amplifies their capabilities and productivity, allowing them to focus on solving real business problems.
Current State of Software Development
What was once a straightforward process of writing and deploying code has evolved into a complex ecosystem of interconnected modules, systems, and services. Let’s look at the key aspects that are shaping the current state of software development.
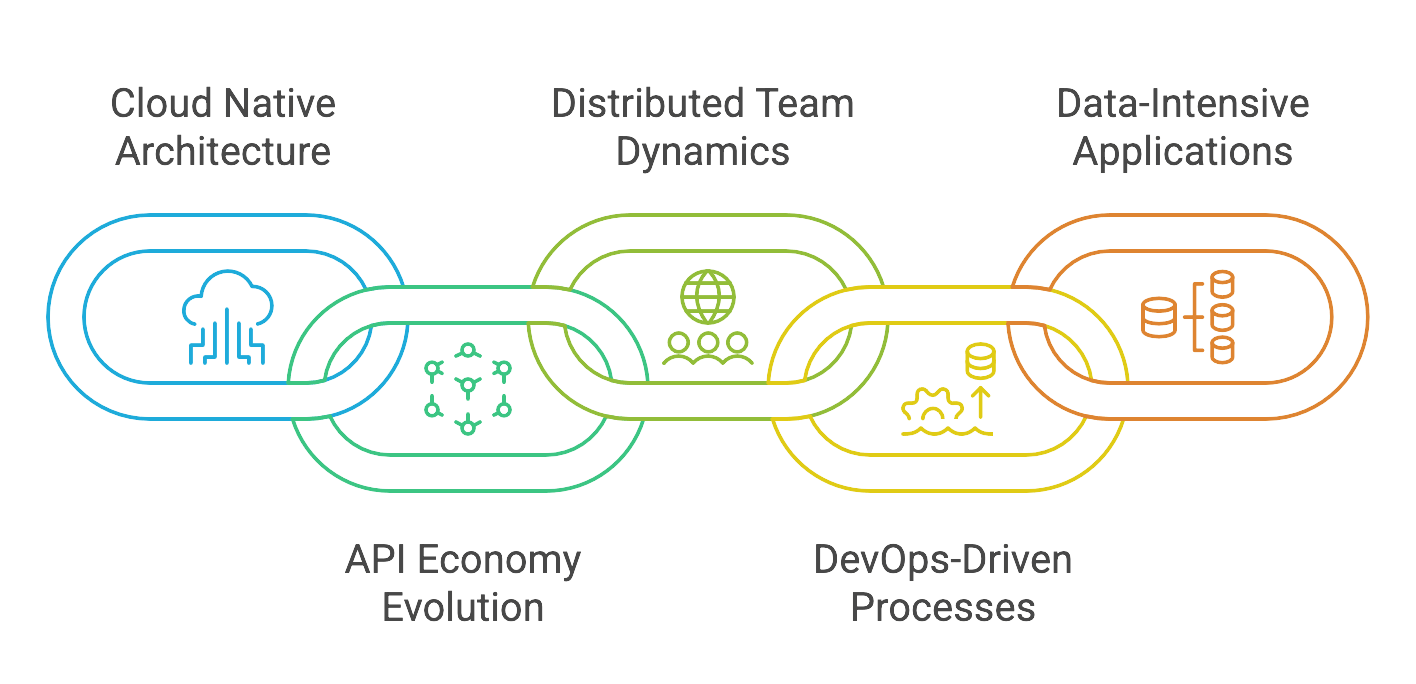
Cloud native architecture
Applications today are composed of multiple microservices, containerized using technologies like Docker and orchestrated through Kubernetes. This allows teams to deploy each service independently, scale efficiently, and maintain high availability. For instance, an e-commerce application can comprise separate microservices for product catalog, shopping cart, and payment processing, each running in isolated containers and communicating using APIs.
API economy evolution
We’ve moved from monolithic applications to microservices-based applications that are interconnected using APIs. Organizations today leverage a mix of internal and external APIs to build applications. A mobile application may interact with an AWS S3 bucket for storage, Stripe for payments, and Auth0 for authentication, creating a complex web of API dependencies.
Distributed team dynamics
Today, teams are more distributed than ever, requiring sophisticated collaboration tools and asynchronous workflows. This requires robust version control practices, comprehensive documentation, and effective communication protocols. Teams rely on Git for version control, Jira for project management, and Slack for asynchronous communication, all while managing remote work, different time zones, and cultural contexts.
DevOps-driven processes
The evolving software development process has blurred the lines between development and operations, and CI/CD pipelines have become standard practice. DevOps and Platform Engineering practices have streamlined the development process end-to-end. A typical pipeline might include GitHub Actions for CI, ArgoCD for CD, Terraform for Infrastructure management, and Prometheus for monitoring.
Data-intensive applications
We’ve all heard the phrase “Data is the new Oil” and modern applications process massive amounts of data in real-time, which requires complex data processing pipelines. Systems must handle both structured and unstructured data, often implementing event-driven architectures with tools like Kafka for streaming and Redis for caching while maintaining performance and data consistency.
Complex dependencies management
Modern applications rely on numerous external libraries, frameworks, and services, creating intricate dependencies. Managing these dependencies is critical and complex as it involves tracking versions, handling vulnerabilities, and ensuring compatibility. Dependency tools like npm for JavaScript and Snyk for scanning have become essential for maintaining healthy and secured code bases.
AI in Software Development
Software development practices have moved from a purely human-driven process to a collaborative effort between developers and AI. With tools like GitHub Copilot, Claude, and Cursor, we see AI integration at every stage of the development lifecycle. This is not just about code generation anymore. It’s about improving developer capability across the SDLC.
Planning
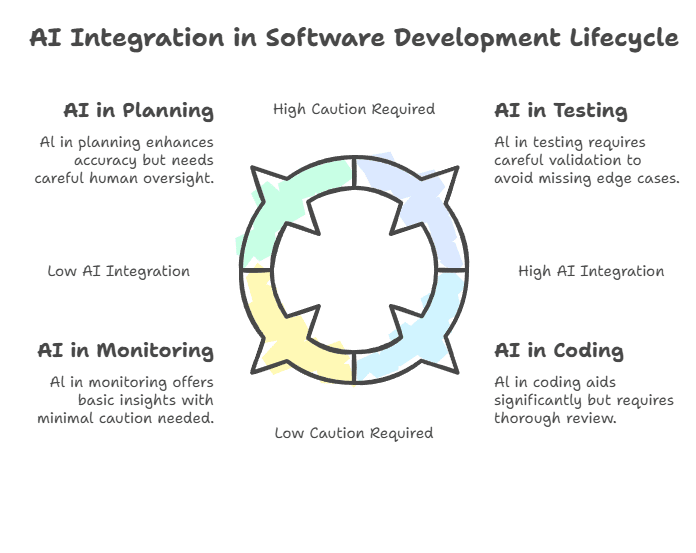
AI brings predictive intelligence to processes like requirement gathering and project scoping. Using natural language processing (NLP) and historical project data, AI tools can analyze requirement documents, suggest user stories, predict bottlenecks, and estimate timelines with increased accuracy.
For instance, teams can use Jira’s AI-powered estimation or Copilot to understand the requirements and plan projects.
Having said that, teams must not overrely on AI-generated estimates or stories. They must also be careful not to ignore the business—and domain-specific constraints and compliance requirements.
Design
Modern AI tools understand your requirements and constraints and can suggest optimal database schemas, API definitions, and infrastructure patterns. By learning from millions of architecture decisions across various projects, AI can now predict scaling challenges, identify potential security vulnerabilities, and recommend best practices.
If you’re on the AWS stack, you can use the AWS Application Compose to visualize all AWS services required for your application. Other tools like Copilot can also come in handy.
However, teams must not blindly accept the generated architectures without considering the scalability and security. Further, AI can oversimplify integration complexity points, so care must be taken to avoid those.
Coding
The impact of AI in coding goes beyond autocomplete. Today’s AI coding assistants understand the context, suggest entire functions, and explain complex code segments. These tools analyze your codebase’s patterns, understand your style, and provide intelligent refactoring suggestions.
Teams can use tools like GitHub Copilot, Amazon’s CodeWhisperer or intelligent IDEs like Cursor and Aider for AI-assisted coding.
Care must be taken to avoid accepting AI-generated code without proper review and overlooking performance implications that may arise.
Testing
AI transforms testing from a reactive process to a predictive one. Modern AI testing tools can automatically generate test cases based on code changes, predict areas most likely to contain bugs, and simulate user behavior patterns. They’re also capable of generating self-healing test scripts, identifying regressions, and even predicting performance bottlenecks.
Teams can use testing tools like Applitools and TestIM for AI-powered testing. If you’re on a cloud-native stack, you can use Testkube for robust continuous testing coupled with AI. AI-powered testing tools can miss edge case scenarios. Hence, teams must not over-rely on the generated tests without human validation.
Monitoring
AI-powered monitoring has evolved from simple alerting to predictive operations. Using machine learning, modern observability tools can detect anomalies before they become incidents, predict resource utilization patterns, and automatically adjust system configuration. They can also analyze complex log patterns, correlate events across distributed systems, and perform comprehensive root cause analysis.
Tools like Dynatrace, New Relic, Datadog, and Grafana provide AI-powered capabilities to their observability platforms.
Such monitoring tools can lead to alert fatigue with oversensitive AI monitoring. Further, automated responses can lose context, which may overlook performance monitoring gaps. At InfraCloud, we used Prometheus and Grafana along with an Nvidia DCGM exporter to monitor our AI Lab.
Considerations & Best Practices
While AI is transforming the software industry, its successful implementation requires careful consideration of several critical factors. These considerations ensure that AI adoption enhances development and aligns with organizational goals, compliance requirements, and security standards.
Security & Data Protection
The integration of AI tools in development lifecycles introduces new security threats. Code snippets shared with AI assistants may leak sensitive information like API tokens, security keys, and proprietary algorithms. For instance, healthcare organizations must abide by HIPAA regulations to protect sensitive patient data, while financial organizations must abide by PCI-DSS to ensure payment details are carefully handled.
Ensure the implementation of data sanitization procedures before AI processing, use private deployments of AI tools for sensitive codebases, and establish clear guidelines for what can be shared with AI assistants.
Process Integration
A successful AI implementation requires seamless integration with your existing development workflows, including CI/CD tools and code review processes. For example, your Agile teams can leverage AI assistants with JIRA to help with sprint planning and development.
It’s critical to validate the integration points of the AI tools you want to implement with your existing tools, such as GitHub, JIRA, or Jenkins, to ensure that AI augments the process without disrupting it.
Cost vs Value Assessment
Implementing AI tools requires careful cost vs. benefit analysis across different organizational contexts. For instance, an AI coding assistant may cost $50+ per developer per month but may reduce development time by 20-30%. This decision can be made based on the industry you’re in. For instance, if you’re in a competitive market, investing in an AI tool will allow you to ship features faster, giving you a competitive advantage.
However, you must take a holistic approach and consider the training costs, potential productivity dips during adoption, incoming code standardization, and long-term maintenance.
Team Readiness and Training
Successful AI implementation depends on how well the team uses it. Organizations must invest in the training and development of their teams to use AI effectively. For instance, developers need training on using AI tools and best practices, AI limitations, effective and prompt engineering, and when to use human expertise. Teams working in the healthcare domain must learn how to use AI while protecting patient data, while those in e-commerce need to know how to optimize performance using AI.
To improve this, organizations can conduct workshops, document prompts and guidelines, and have mentorship programs for training teams. We’ve created dedicated Slack channels at InfraCloud where we share AI-related tools and learnings and conduct regular workshops to upskill our teams.
Quality Control Frameworks
Robust checks must be in place for AI-generated code. Organizations must establish clear review protocols for AI outputs, automated testing requirements, and performance benchmarks. For instance, banking software teams might require additional security scanning for AI-generated code, while real-time systems need strict performance verification.
Validating metrics like code quality, number of bugs, and development velocity and enabling a feedback loop is critical.
Governance & Compliance
Comprehensive governance frameworks for AI tool usage that align with industry best practices must be in place. Financial services must ensure AI usage complies with GDPR and CCPA, while healthcare software needs HIPAA alignment. Create policies about AI tool usage, data sharing, and code ownership. Implement audit trails for AI-assisted development, regular compliance checks, and clear escalation paths for governance issues.
Consider industry-specific requirements like SOC2 for cloud services or ISO for manufacturing industries.
Embracing AI-enabled future
AI integration in software development represents a fundamental shift in application building and deployment. The boundary between AI assistance and human expertise continuously evolves as tools gain contextual understanding, reliable code generation, and deeper analytical capabilities.
The key for teams looking to begin their AI-enabled development journey is to start small and scale strategically. Begin by identifying specific pain points where AI can immediately impact—whether it’s code completion, automated testing, or enhanced code reviews. Smart developers don’t just code; they leverage AI to build better, faster, and more intelligent applications. At InfraCloud, we regularly share blog posts and conduct webinars on complex topics of artificial intelligence. If you are looking to leverage AI workflows to improve your developers’ productivity, our AI cloud experts can help you with it. Do share your thoughts on this article and how you use AI, as well as any interesting use cases that you have with me on LinkedIn.
The future of software development is here, and it’s AI-enabled. Are you ready to get started?
Stay updated with latest in AI and Cloud Native tech
We hate 😖 spam as much as you do! You're in a safe company.
Only delivering solid AI & cloud native content.